
72 核的Grace CPU
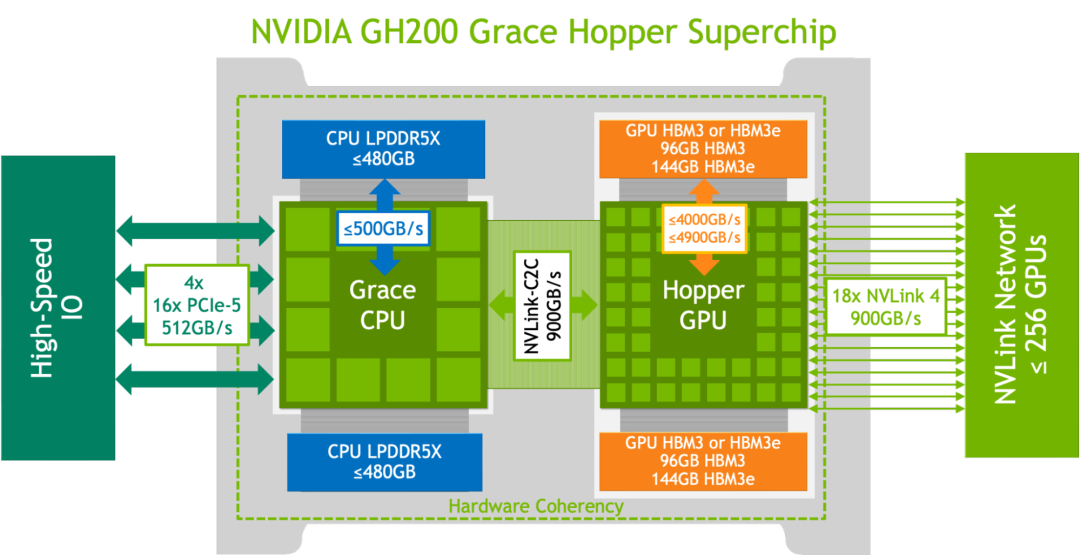
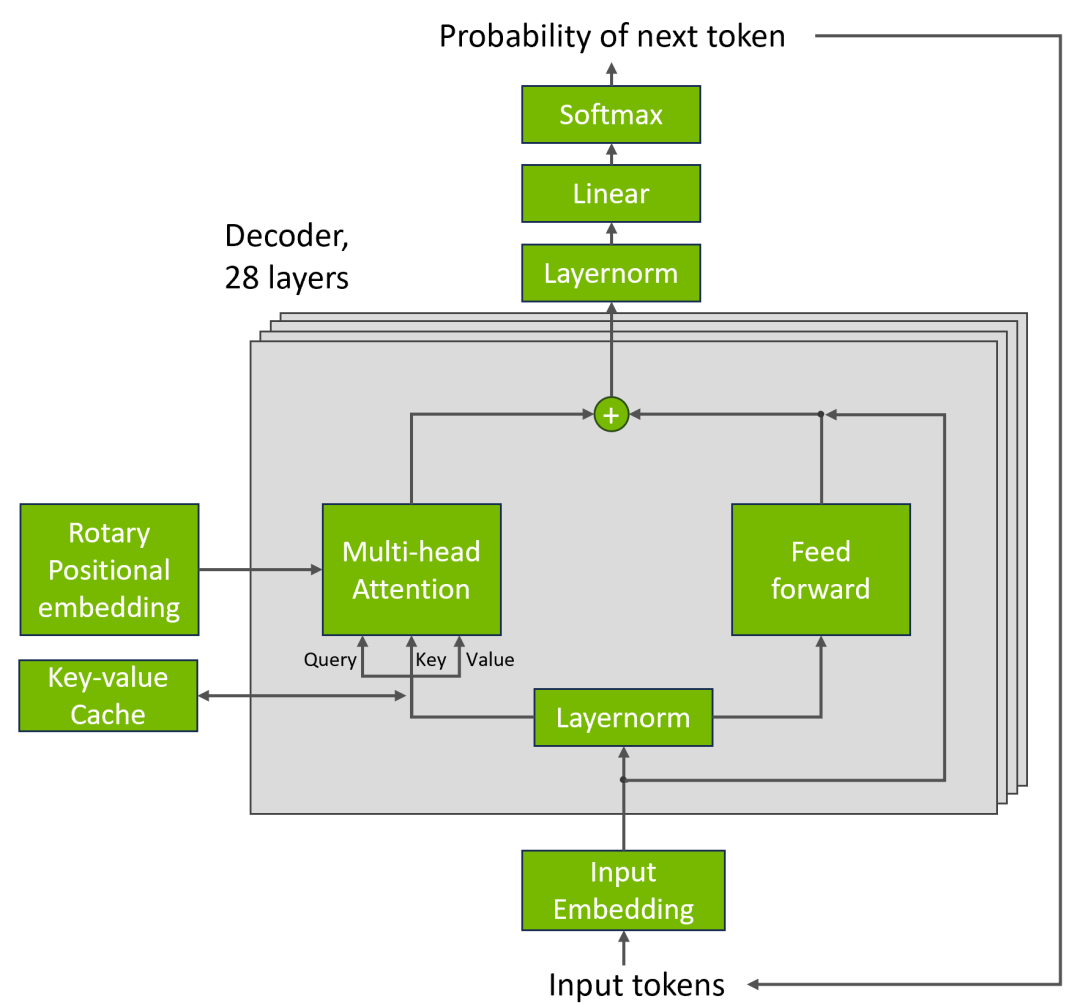
Logical overview of the NVIDIA GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip
GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip 采用 96 GB HBM3,并提供高达 4 TB/s 的 HBM3 内存带宽,而 H100 SXM 分别为 80 GB 和 3.35 TB/s。 与 NVIDIA H100 SXM 相比,更大的内存容量以及更大的内存带宽使得 NVIDIA GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip 上的工作负载能够使用更大的批量大小。 例如,RetinaNet 和 DLRMv2 在服务器场景中以高达两倍的批处理大小运行,在离线场景中以大 50% 的批处理大小运行。
GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip NVIDIA Hopper GPU 和 Grace CPU 之间的高带宽 NVLink-C2C 链路可实现 CPU 和 GPU 之间的快速通信,从而有助于提高性能。
例如,在 MLPerf DLRMv2 工作负载中,通过 PCIe 传输一批张量大约需要 H100 SXM 上批量推理时间的 22%。 然而,GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip 仅使用 NVLink-C2C 的 3% 的推理时间来执行相同的传输。
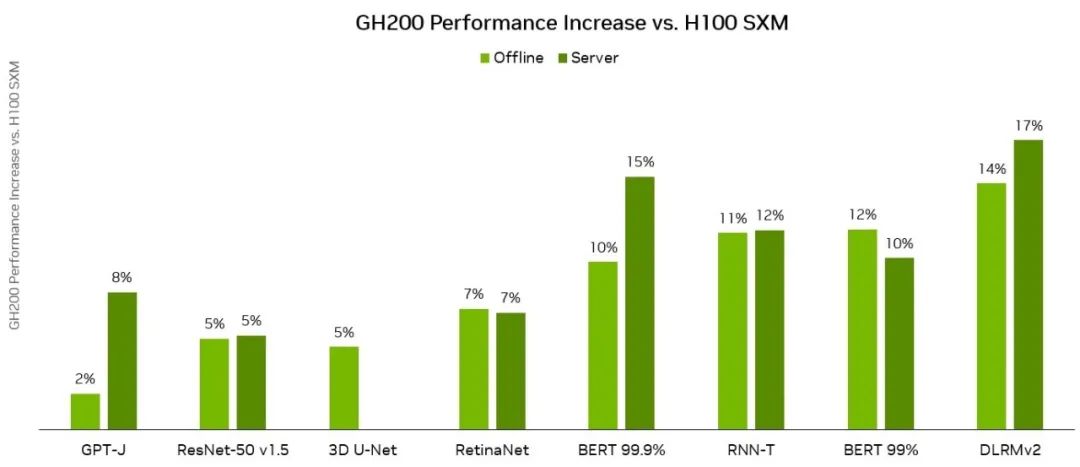
得益于更高的内存带宽和更大的内存容量,与 H100 GPU 相比,Grace Hopper Superchip 在 MLPerf Inference v3.1 工作负载上的每芯片性能优势提高了 17%。 这些结果展示了 GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip 和 NVIDIA 软件堆栈的性能和多功能性。
To represent LLM inference workloads, MLPerf Inference v3.1 introduces a new test based on the GPT-J 6B model: an LLM with 6B parameters. The task tested by the new benchmark is text summarization using the CNN/DailyMail dataset.
为了表示 LLM 推理工作负载,MLPerf Inference v3.1 引入了基于 GPT-J 6B 模型的新测试:具有 6B 参数的 LLM。 新基准测试的任务是使用 CNN/DailyMail 数据集进行文本摘要。
The NVIDIA platform delivered strong results on the GPT-J workload, with GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip delivered the highest per-accelerator performance on both the Offline and Server scenarios on a per-accelerator basis. The NVIDIA L4 GPU also delivered strong performance, outpacing the best CPU-only result up to 6x in a 1-slot PCIe card with a thermal design power (TDP) of just 72 Watts.
NVIDIA 平台在 GPT-J 工作负载上取得了出色的成绩,其中 GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip 在离线和服务器场景中以每个加速器为基础提供了最高的每个加速器性能。 NVIDIA L4 GPU 还提供了强大的性能,比 1 插槽 PCIe 卡中仅使用 CPU 的最佳结果高出 6 倍,热设计功耗 (TDP) 仅 72 瓦。
To achieve these results, NVIDIA software for LLM inference intelligently applies both FP8 and FP16 precisions to increase performance while also meeting target accuracy requirements.
为了实现这些结果,用于 LLM 推理的 NVIDIA 软件智能地应用 FP8 和 FP16 精度来提高性能,同时满足目标精度要求。
A key challenge for performing GPT-J inference is the high memory consumption of the key-value (KV) cache in the transformer block. By storing the KV cache in the FP8 data format, the NVIDIA submission significantly increased the batch size used. This boosted GPU memory utilization and enabled better use of the immense compute performance of NVIDIA GPUs.
执行 GPT-J 推理的一个关键挑战是转换器块中键值 (KV) 缓存的高内存消耗。 通过以 FP8 数据格式存储 KV 缓存,NVIDIA 提交的文件显著增加了所使用的批量大小。 这提高了 GPU 内存利用率,并能够更好地利用 NVIDIA GPU 的巨大计算性能。
要驱动这个怪兽级异构计算平台,依赖于NVIDIA在“计算软件栈”深厚的功力。